Economic Individual Assignment
Tan Hui Nee 0309696 Section 11
Garment industry is the makers and sellers of fashionable clothing. Nowadays,
this industry is very competitive in the markets due to the increasing of
garment firms. Garment
industry might consist of five distinct and separate levels such as haute couture,
luxury wear, affordable luxury wear, mainstream clothing, and discount clothing
(Thefreedictionary, 2009). There
are many brands in the market with different price level. The increasing number
of the garment firms has increased the range of people choice.
Large number of firms


 According to Mankiw and Taylor (2011), monopolistic
competition is a market structure that the firm selling the same product but
slightly different .In monopolistic competition, it consists of many sellers in
a specific industry. The firms are competing among them. For example, garment
industry. Garment industry known as monopolistic firm is because there are many
different brand garment firms competing in the market such as Zara, GAP, Mango,
H&M, Esprit, ELLE, Padini Concept Store and others. This actually denotes
that monopolistic firms have small market share in the firm which has empowered
to influence the price of the product because of the brand loyalty. In this
case, we should think about why brand loyalty can influence the price setting
of a garment firms? The reason is when customers are loyal to a brand; price
will not be the issue for them. Hence, when the price of a garment increase,
people will still buying the garment. Moreover, monopolistic competition firms
are behaving independently among their competitors. Behaving independently
means that the prices or the strategy that one of the monopolistic firms used
will not direct affect other competitors. This is because monopolistic firm
will still survive at the end of the day due to differentiated product and
brand loyalty. When the product is differentiated, collusion of the product is
definitely impossible to happen.
According to Mankiw and Taylor (2011), monopolistic
competition is a market structure that the firm selling the same product but
slightly different .In monopolistic competition, it consists of many sellers in
a specific industry. The firms are competing among them. For example, garment
industry. Garment industry known as monopolistic firm is because there are many
different brand garment firms competing in the market such as Zara, GAP, Mango,
H&M, Esprit, ELLE, Padini Concept Store and others. This actually denotes
that monopolistic firms have small market share in the firm which has empowered
to influence the price of the product because of the brand loyalty. In this
case, we should think about why brand loyalty can influence the price setting
of a garment firms? The reason is when customers are loyal to a brand; price
will not be the issue for them. Hence, when the price of a garment increase,
people will still buying the garment. Moreover, monopolistic competition firms
are behaving independently among their competitors. Behaving independently
means that the prices or the strategy that one of the monopolistic firms used
will not direct affect other competitors. This is because monopolistic firm
will still survive at the end of the day due to differentiated product and
brand loyalty. When the product is differentiated, collusion of the product is
definitely impossible to happen.
Product differentiation
Since
monopolistic firm consists of many sellers in competing with each other, they
produce differentiated product to make themselves exclusive. In differentiated
product, there is close substitute instead of perfect substitute ( Bade and
Parkin, 2009).The firm produce goods that customers can differentiate and also
benefits customers form having variety of goods (Investopedia, 2013). When the
products can be differentiated by buyers, it might satisfy the buyers. Brand
loyalty might accomplish. Hence, the firms can actually generate economic profit
in the short-run. Cloth is differentiated product which we can differentiate it
by price, brand, quality, trend, seasons and material used. In the perspective
of a buyer, when you pay for a high price, definitely you might refer to the
quality and brand worth for it or not. For example, Mango, Zara and FOREVER 21
they produce differentiated garments. So, when the price of Mango increased,
buyer might shift to Zara and FOREVR 21. Consequently, Mango will generate
lesser economic profit. The link below mentioned
how Zara differentiate its product by fashion trend and customers’ taste
http://edition.cnn.com/BUSINESS/programs/yourbusiness/stories2001/zara/http://edition.cnn.com/BUSINESS/programs/yourbusiness/stories2001/zara/
Firms are competing on product quality, price and
marketing
In such competitive market, product quality, price and
the marketing strategy used might be the concern for monopolistic firms to
attract potential customers and accomplish brand loyalty. In garment industry,
quality can be referred to the comfort of its garment. There might be same
design of clothes but different quality in the market based on the material
used. Sometimes, some firms are using cheaper cotton to lower their cost of production
while some firms are using better quality cotton. Hence, differentiation of the
garment actually creates competition between each of the brand. In monopolistic
firms, they may compete between each other, but, they are not really emphasized
on the price of goods they produce. The firms will be emphasized more on making
their product exclusive than their competitors. Therefore, it is a compulsory
for monopolies firms to advertise their product due to the product is differentiated.
The features of the product are important to inform the buyers through the
advertising or packaging. For example, Padini had advertised it product by
video follow the summer theme. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eICyZWIUXD4.
By advertising, the demand for Padini cloth might become elastic and the price
will become cheaper.
Low Barrier to entry and exit
As mentioned
above, monopolistic competition consists of many sellers. Therefore, new firms
might come in easily to compete. This is because the firms are too small to
block people from coming in. Nowadays, there are more and more firms that
starting online trade like selling clothes. There are low barriers to entry or
exit for them. Moreover, when the firm decreases their price, definitely
economic profit will decrease. However, when the firm makes losses, they can
make decision to leave the firm. As the firm exit, it might boost the profits
and prices of remaining firm. Therefore, it can eliminate the losses for the
remaining firm. However, in the long-run, firms neither leave nor entry the
industry because it generates zero profit in the long run (Bade and Parkin,
2009).
The figure above show the normal profit in the long-run of Monopolistic firm. It incurred when the P= ATC.
Is Monopolistic Competition Efficient?
In monopolistic competition, it is one of the market structures that can
be efficient and inefficient in two different situations. Monopolistic
competition generally charged higher price and produce lesser product. Just
like in garment industry, they sometimes limited the production of clothes. So,
when the clothes are out of stock, they can push the price higher. This actually
benefits the firm in making economic profits. When a market is inefficient, it
mean that one firm is under produce. In
this market structure, the firm tends to control the quantity produce. So, they
can push the price higher.
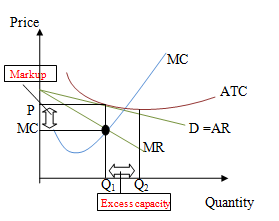
Look at the graph above, it show the markup and the excess capacity. Monopolistic competition is not allocated efficiency. This
is because the inefficiency found in the market control and negatively-slope
demand curve. The demand curve downward sloping implies that the price is
higher than the marginal cost (Amosweb, 2013). In profit-maximizing, the marginal
cost is equal to marginal revenue which is the efficient price. But the firm do
have the power to charge higher price. Thus, the gap between Marginal cost and
price is call as mark-up. The inequality between price and marginal cost is the
reason that monopolistic competition is inefficient. Other than that, the firms
have the power to produce less than the efficient quantity. Q1 is
the quantity that the firm willing to produce while Q2 is the
efficient quantity which touches the minimum ATC. Therefore, excess capacity
incurred. In another word, excess capacity is the differences between the efficient
quantity and the quantity the firms willing to produce. Because of price
exceeds marginal cost, the economy gives up less satisfaction from other goods
not produced than it receives from the good that is produced. The economy can
gain satisfaction by producing more of the good (Amosweb, 2013). This is
applicable in the link: http://www.wellheeledblog.com/2009/08/22/profit-margins-in-fashion-industry-banana-republic/.
Banana Republic has mark-up its price to $98. But, after the discounts, it only
cost $20.
REFERENCES:
Amosweb.com. 2013. AmosWEB is Economics:
Encyclonomic WEB*pedia. [online] Available at:
http://www.amosweb.com/cgi-bin/awb_nav.pl?s=wpd&c=dsp&k=monopolistic+competition,+efficiency
[Accessed: 8 Jun 2013].
Bade, R. and Parkin, M. 2009. Foundations of Economics. 4th ed. United States of America: Pearson, p.408.
Investopedia.com. 2013. Monopolistic Competition
– CFA Level 1 | Investopedia. [online] Available at:
http://www.investopedia.com/exam-guide/cfa-level-1/microeconomics/monopolistic-competition.asp
[Accessed: 8 Jun 2013].
Mankiw, N. and Taylor, M. 2011. Economics.
2nd ed. South Western: Cengage Learning.
TheFreeDictionary.com. 2009. garment
industry. [online] Available at:
http://www.thefreedictionary.com/garment+industry [Accessed: 8 Jun 2013].